In the world of cybersecurity, vulnerabilities can pose a significant risk to businesses. It is essential to patch any vulnerabilities in a timely manner to prevent cyber attackers from exploiting them. However, patching can be difficult, especially when the system with the vulnerability is outside of your direct control. In such cases, virtual patching can save the day.
Virtual patching is a cybersecurity concept that involves implementing a security control mechanism to limit the risks associated with existing vulnerabilities, particularly when patching is not feasible or may take too much time. Essentially, virtual patching involves placing a layer of protection around vulnerable systems to prevent malicious payloads from exploiting them.
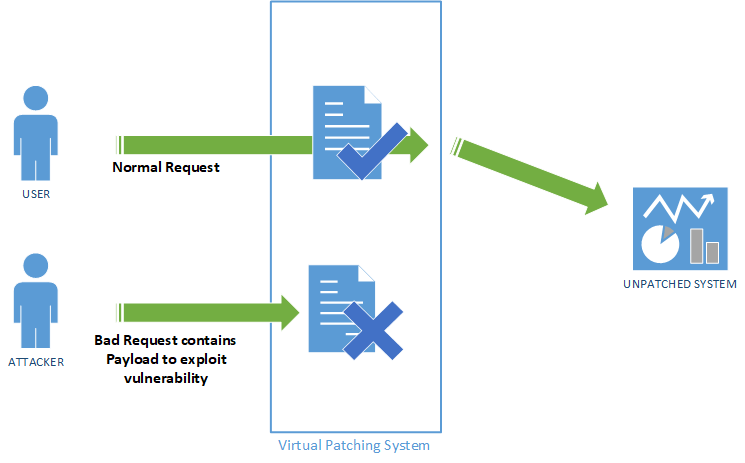
One of the main advantages of virtual patching is its ability to quickly implement security controls and reduce the risk level associated with a vulnerability. This is particularly useful in situations where patching is not feasible due to operational continuity issues, limited visibility, or the presence of legacy systems that cannot be patched.
In the Azure platform, virtual patching can be achieved through various tools and services such as intermediary devices like web application firewalls (WAF) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), as well as hardening measures on the application side.
When it comes to Azure, there are several tools and services that can be used for virtual patching. One such tool is Azure Security Center, which provides a unified security management solution that helps identify and remediate vulnerabilities in Azure resources.
Another service that can be used for virtual patching on Azure is Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF). Azure WAF is a security feature that helps protect web applications from common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Azure WAF allows you to create rules to filter web traffic based on conditions such as IP addresses, HTTP headers, and custom URIs, thereby providing an additional layer of protection against web attacks.
Furthermore, Azure Security Center also supports third-party solutions for virtual patching, including Fortinet, Check Point, and Trend Micro. These vendors provide virtual patches through their predefined rules that can be easily applied to your Azure resources, thereby reducing the risks of exploitation.
In addition to Azure WAF and Azure Security Center, Azure Firewall is another service that can be used for virtual patching on Azure. Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based network security service that provides network traffic filtering and routing capabilities for Azure resources. It can be used to create network security rules to block traffic from known malicious IP addresses, thereby providing an additional layer of protection against cyber attacks.
Azure, Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, offers a variety of services that can help with virtual patching. Let’s take a closer look at some of them.
Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Azure WAF provides an additional layer of protection for web applications. It filters web traffic based on conditions such as IP addresses, HTTP headers, and body, or custom URIs. With Azure WAF, you can create custom rules to block common web exploits like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
Azure WAF also offers managed rules provided by third-party vendors like Barracuda, Imperva, and Fortinet. These managed rules offer a quick and easy way to implement virtual patches for known vulnerabilities.
Azure Security Center
Azure Security Center provides a unified view of your security posture across Azure and on-premises environments. It offers continuous security assessment and recommendations for improving security. Azure Security Center also provides virtual patching for known vulnerabilities.
For example, in the case of the Log4j vulnerability, Azure Security Center offers a recommendation to install a virtual patch to block the exploitation of the vulnerability. You can also configure Azure Security Center to automatically apply virtual patches for known vulnerabilities.
Azure Firewall
Azure Firewall is a cloud-native network security service that offers high availability and scalability. It provides inbound and outbound network filtering to protect your resources. With Azure Firewall, you can create custom rules to block traffic to and from known malicious IP addresses.
You can also use Azure Firewall to create virtual patches for known vulnerabilities by blocking traffic to and from the vulnerable component.
Azure Defender for IoT
Azure Defender for IoT is a cloud-native security solution for IoT devices. It provides threat detection and response capabilities to protect your IoT devices from cyber attacks. Azure Defender for IoT also offers virtual patching for known vulnerabilities in IoT devices.
For example, if you have a vulnerable IoT device that cannot be patched, Azure Defender for IoT can create a virtual patch by blocking traffic to and from the vulnerable component.
In conclusion, virtual patching is a crucial part of a comprehensive vulnerability management strategy. Azure offers a variety of services that can help with virtual patching, including Azure Web Application Firewall, Azure Security Center, Azure Firewall, and Azure Defender for IoT. By leveraging these services, businesses can protect their systems from known vulnerabilities even when patching is not possible.
